diff options
| author | Christian Kolset <christian.kolset@gmail.com> | 2025-04-03 14:59:39 -0600 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Christian Kolset <christian.kolset@gmail.com> | 2025-04-03 14:59:39 -0600 |
| commit | 75bfe5fd2284a1a904d46d41764c650fbf86ac8b (patch) | |
| tree | acd9e4494c960b6f4ad9fbc8993d2592ede05e60 /tutorials/module_2 | |
| parent | c686d921c025489a3abde85bc42fac8b6484140d (diff) | |
Added Module 3 and updated mod2/version_control.md
Diffstat (limited to 'tutorials/module_2')
| -rw-r--r-- | tutorials/module_2/2_version_control.md | 19 |
1 files changed, 12 insertions, 7 deletions
diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/2_version_control.md b/tutorials/module_2/2_version_control.md index 5526e2e..d2b4ae8 100644 --- a/tutorials/module_2/2_version_control.md +++ b/tutorials/module_2/2_version_control.md @@ -64,10 +64,7 @@ Here is a list of some git commands to get you started. Interested in learning more about git? Here's a free book that teaches you everything about git and how to use it at a professional level. Available as both HTML and PDF download: [Git Pro](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2). -## How to use Git to - - -## GitHub - Collaborative Projects +## GitHub - The collaborative platform GitHub is a web-based platform that hosts Git repositories and provides collaboration tools for developers. It allows developers to share code, track issues, and collaborate on projects with other developers. GitHub is widely used for open-source projects, team collaboration, and code hosting. ### GitHub Features - Remote Repository Hosting - GitHub allows you to host projects and code remotely on their servers. @@ -76,20 +73,25 @@ GitHub is a web-based platform that hosts Git repositories and provides collabor ### Workflow Depending on the size of the project and whether the project is closed- or open-source, the workflow of the project will differ. In this section we cover some git workflow models and the model you're going to be using for this course. + **Centralized**: The project has only one central hub or *repository*, can accept code and everybody synchronizes their work with it. This model is suitable for small and closed-sourced projects. 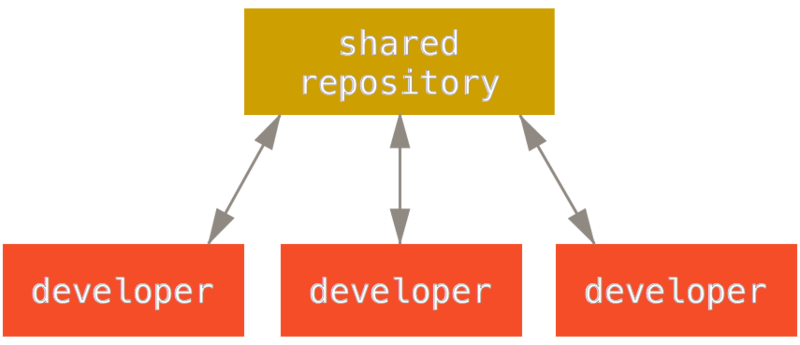 + **Integration-Manager:** There are multiple public variants of the code original code known as *forks*. The integration manager can decide what features to pull from the forks. This is the model that is similar to the one used on GitHub 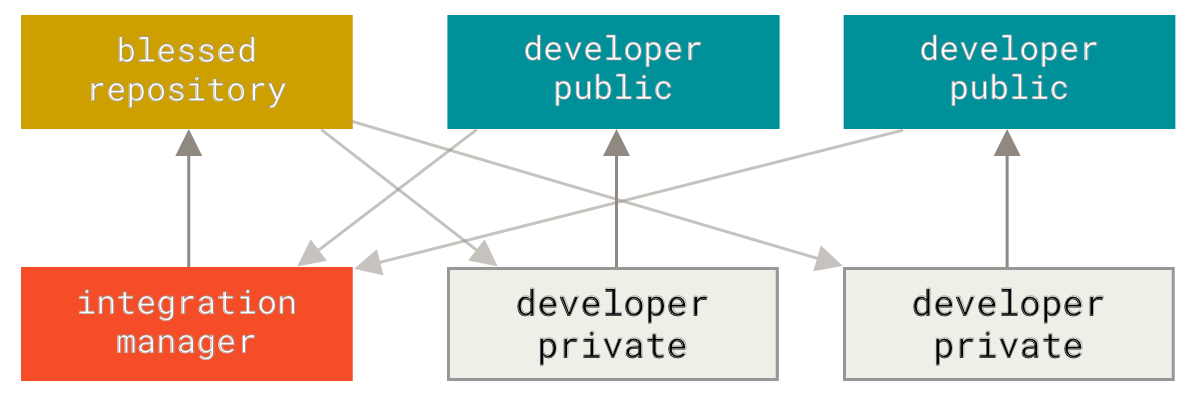 + **Dictator and Lieutenants Workflow:** This is similar to the integration-manager model, however due to the size of the project. A rank of integration managers is formed. one example of this is the development of the Linux kernel. 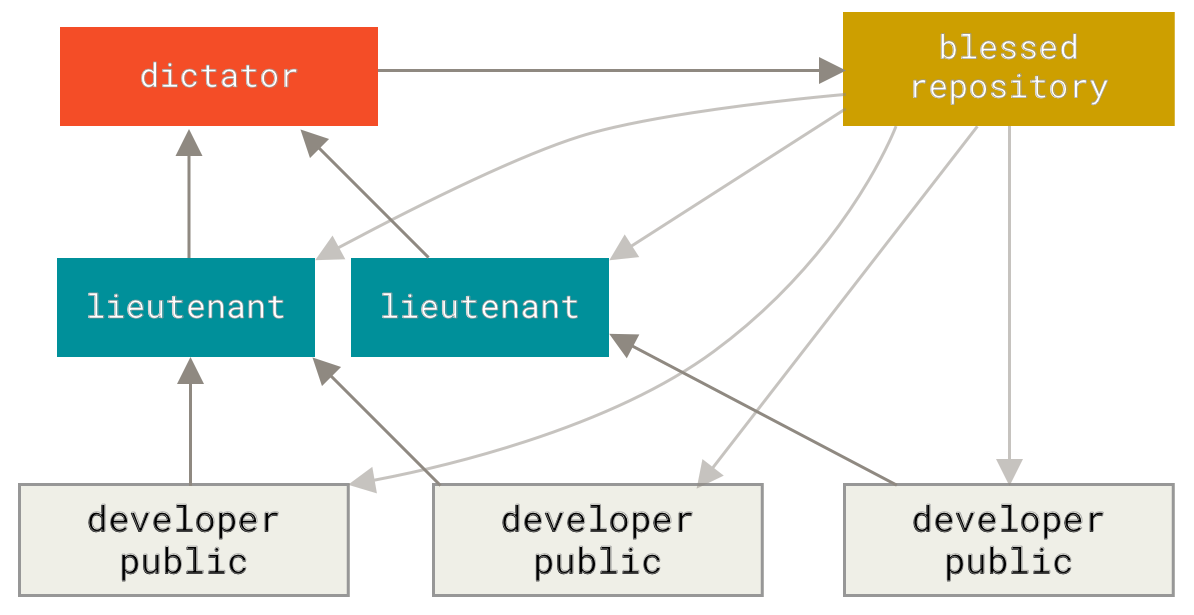 GitHub is designed around a particular collaboration workflow, centered on Pull Requests. This flow works whether you’re collaborating with a tightly-knit team in a single shared repository, or a globally-distributed company or network of strangers contributing to a project through dozens of forks. It is centered on the Topic Branches workflow covered in Git Branching. + + Here’s how it generally works: 1. Fork the project. 2. Create a topic branch from master. @@ -101,7 +103,10 @@ Here’s how it generally works: 8. Sync the updated master back to your fork. ### Terms -- Pull Request - A pull request is a request to merge changes from a feature branch into the main branch. -- Merge - Merging combines the changes from one branch into another branch. -- Conflict - A conflict occurs when Git cannot automatically merge changes and requires manual intervention. +- Pull Request - A *pull request* is a request to merge changes from a feature branch into the main branch or from a forked repository to the original or "upstream" repository. +- Merge - A *merge* combines the changes from one branch into another branch. +- Conflict - A *conflict* occurs when Git cannot automatically merge changes and requires manual intervention. + +### Code resource - Using GitHub to re-use existing code. +In your engineering career, you will most likely use a method of computation that has been done before. In such scenarios, open-source |
