diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'tutorials/module_2/version_control.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | tutorials/module_2/version_control.md | 11 |
1 files changed, 5 insertions, 6 deletions
diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md b/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md index 78b90db..7d633a5 100644 --- a/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md +++ b/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md @@ -11,7 +11,6 @@ In the open-source community VCS is the In this section is divided up into two major sections. The first section *Git* will cover the basics of how to create backups of your project. The second section will cover how to use git with GitHub to *collaborate* on projects. ---- ## Git Git is a version control program that tracks changes to files and directories using snapshots. It is a distributed version control system, meaning that each developer has a complete copy of the repository on their local computer. Git is the most widely used version control system and is popular among developers for its speed, flexibility, and efficiency. @@ -24,13 +23,13 @@ Pay attention now — here is the main thing to remember about Git if you want t This leads us to the three main sections of a Git project: the working tree, the staging area, and the Git directory. -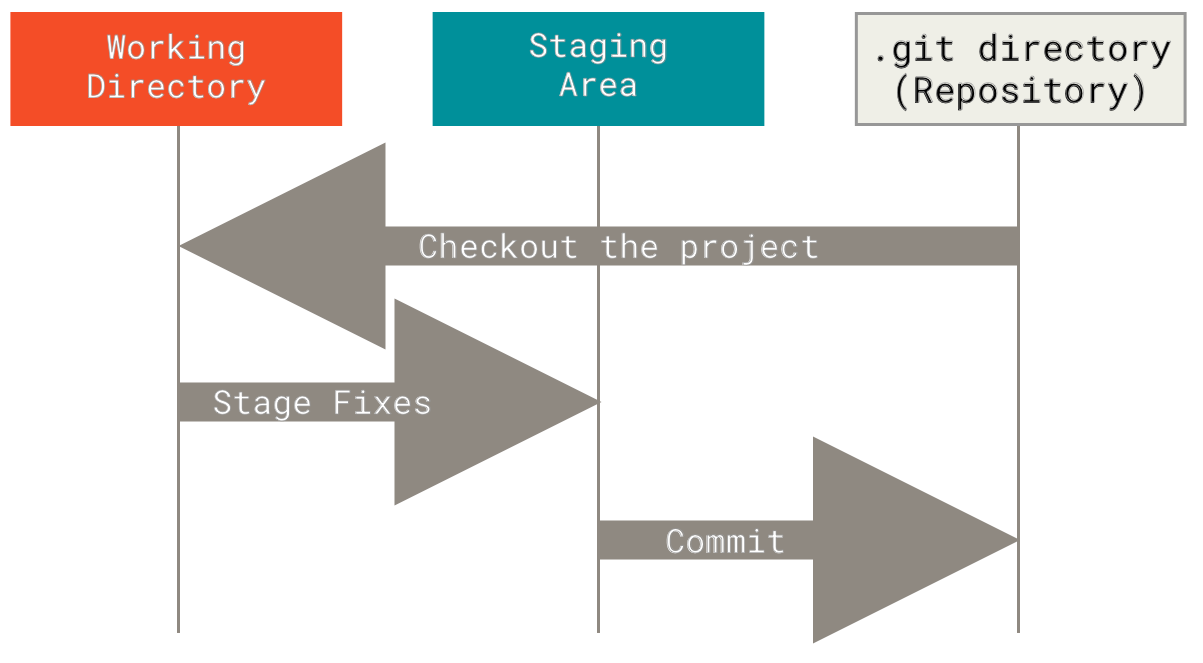 + ### Branching In git, branches allow for parallel workflow on a project. It give contributors the ability to work different features at the same time. Each branch represents an independent line of development, and once a feature or fix is complete, it can be merged back into the main branch. Here is a common branching structure used in many Git projects: - Main Branch - The main branch (a.k.a. master branch) is the default branch in a Git repository and contains the stable version of the code. - Development Branch - is created to develop a new feature or fix a bug without affecting the main branch. It isn’t necessarily always stable, but whenever it gets to a stable state, it can be merged into master. - Topic Branch - A topic branch is a short-lived branch that you create and use for a single particular feature or related work. -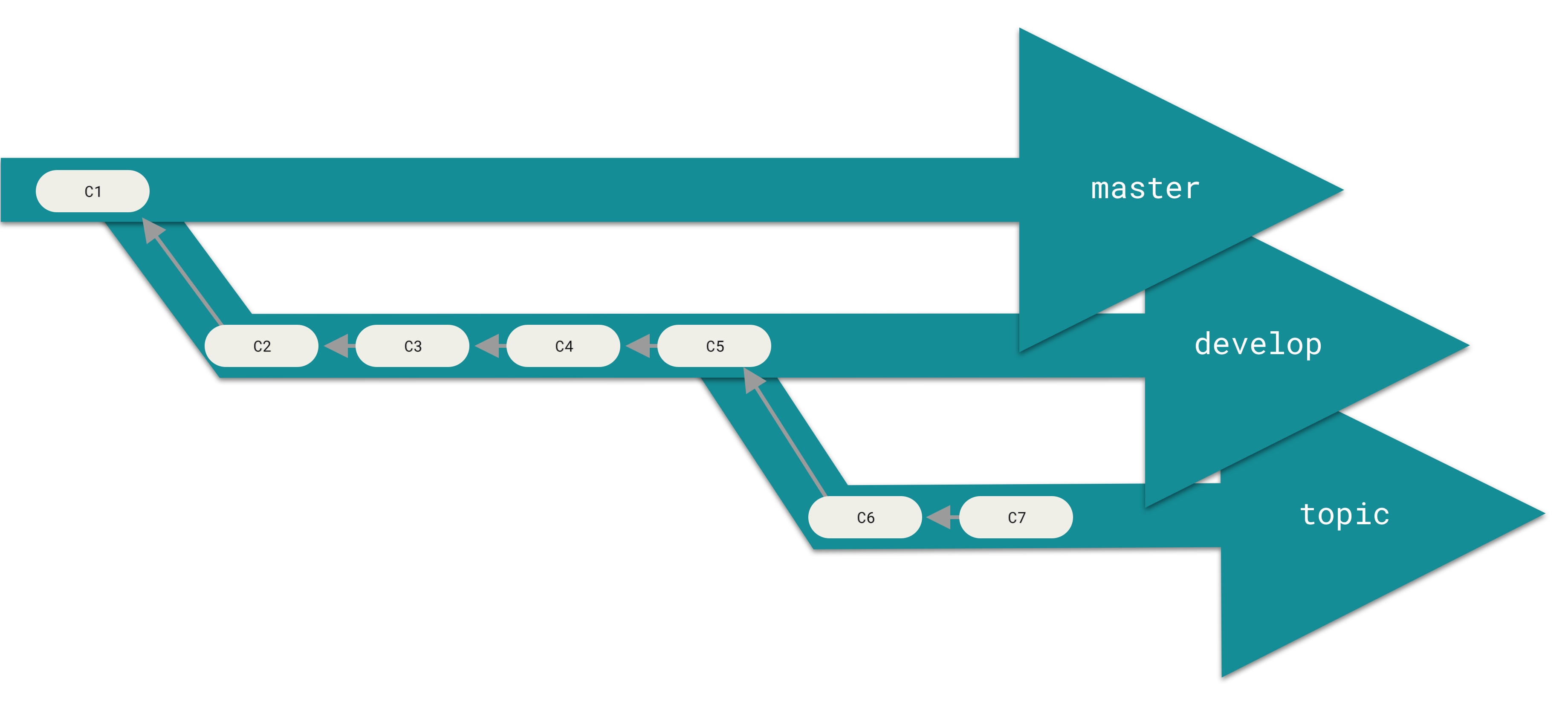 + ### Best Practices - Use descriptive commit messages. - Commit early and often. @@ -75,17 +74,17 @@ Depending on the size of the project and whether the project is closed- or open- **Centralized**: The project has only one central hub or *repository*, can accept code and everybody synchronizes their work with it. This model is suitable for small and closed-sourced projects. -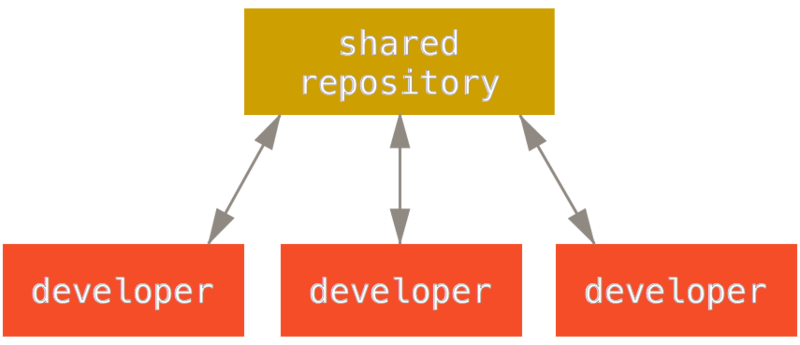 + **Integration-Manager:** There are multiple public variants of the code original code known as *forks*. The integration manager can decide what features to pull from the forks. This is the model that is similar to the one used on GitHub -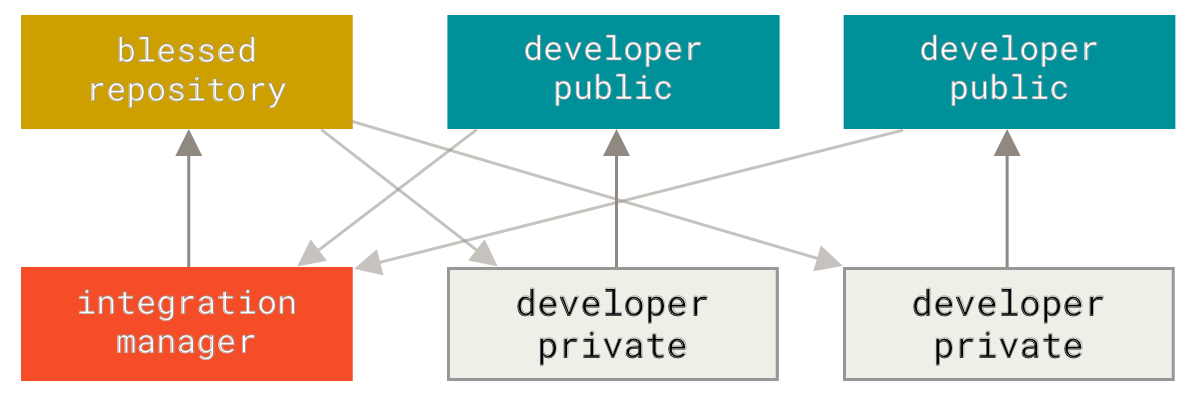 + **Dictator and Lieutenants Workflow:** This is similar to the integration-manager model, however due to the size of the project. A rank of integration managers is formed. one example of this is the development of the Linux kernel. -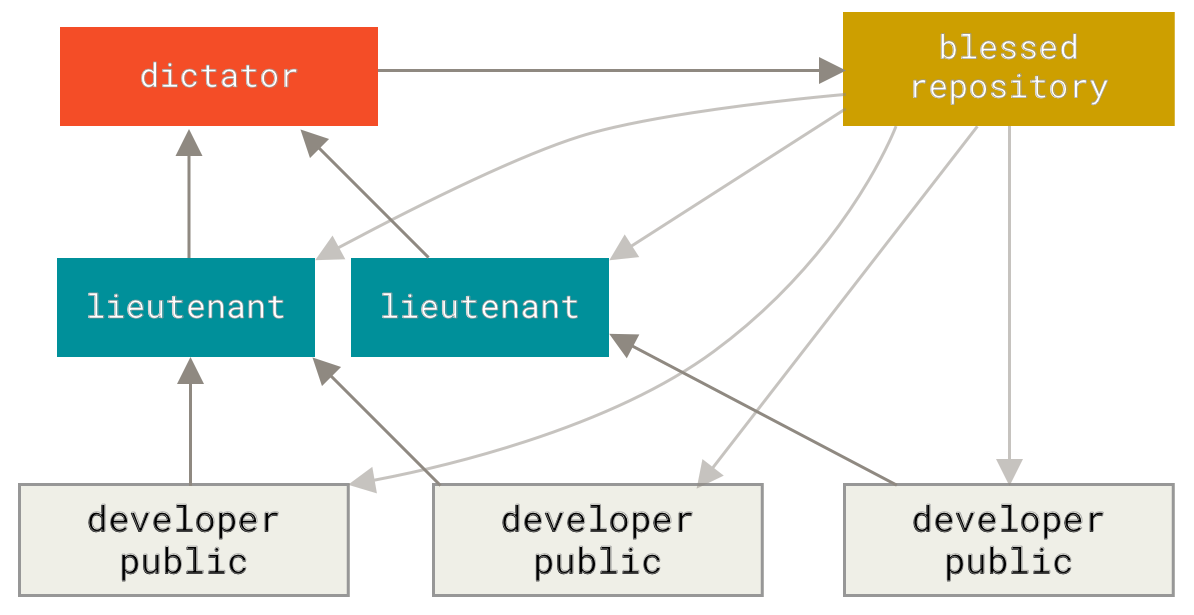 + GitHub is designed around a particular collaboration workflow, centered on Pull Requests. This flow works whether you’re collaborating with a tightly-knit team in a single shared repository, or a globally-distributed company or network of strangers contributing to a project through dozens of forks. It is centered on the Topic Branches workflow covered in Git Branching. |
