diff options
| author | Christian Kolset <christian.kolset@gmail.com> | 2025-04-24 16:25:31 -0600 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Christian Kolset <christian.kolset@gmail.com> | 2025-04-24 16:25:31 -0600 |
| commit | 652f88728eb91bae1c4f30b63d1fbe60788ea938 (patch) | |
| tree | 65cfe591da183b969885e8c557b1ac5810727ec8 /tutorials/module_2 | |
| parent | 42fca6122f4baf847ec2794b172abbc6a2193407 (diff) | |
Added jupyter notebook converter script. Converts markdown (.md) tutorials to jupyter notebook (.ipynb).
Diffstat (limited to 'tutorials/module_2')
4 files changed, 447 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/ai_assisted_programming.ipynb b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/ai_assisted_programming.ipynb new file mode 100644 index 0000000..8004e91 --- /dev/null +++ b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/ai_assisted_programming.ipynb @@ -0,0 +1,73 @@ +{ + "cells": [ + { + "cell_type": "markdown", + "metadata": {}, + "source": [ + "# AI Assisted Programming\n", + "\n", + "## What is it?\n", + "\n", + "Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been around for a long time. However,\n", + "not until recently did engineers make it easy and “fun” to work with. By\n", + "now you probably have a pretty good idea of what AI can do. However, you\n", + "may not have used an AI assistant before. As the name suggests, an AI\n", + "assistant can help you develop code, speed up your writing with code\n", + "suggestions and allows you to focus on solving the problem at hand\n", + "rather. AI is a technology that is constantly improving. As engineers we\n", + "need to *understand* how we can use AI as a tool to achieve our goals\n", + "more efficiently. This section cover good practices of how we can\n", + "implement AI and lists some AI assistant tools that we can use. \\## Good\n", + "vs. Bad uses of AI Don’t try to get AI to do work *for you* but *with\n", + "you*. You need to understand what you’re doing. If you don’t understand\n", + "what the AI is doing, then you’re not in control of the work. You’re not\n", + "going to go far until something unexpected happens.\n", + "\n", + "AI is a great learning tool, research as show that students can benefit\n", + "from using AI as personal tutor\n", + "[more](https://hbsp.harvard.edu/inspiring-minds/ai-as-personal-tutor).\n", + "\\## Available tools Below is a comprehensive list of tools that are\n", + "available at not cost to you.\n", + "\n", + "| Name | Features |\n", + "|----------------|----------------------------------------------------|\n", + "| GitHub Copilot | Paid, but free for students. Integrated in GitHub. |\n", + "| ChatGPT | Free, optional paid upgrade |\n", + "| Grok | Free, optional paid upgrade |\n", + "| Gemini | Free, optional paid upgrade |\n", + "| GPT4ALL | Free and Open-Source |\n", + "| Code GPT | Free and Open-Source |\n", + "| Cody | Free and Open-Source |\n", + "| DataLab AI | Free |\n", + "| Codeium | Free |\n", + "| aiXcoder | Free |\n", + "\n", + "Many of the tools above come with similar, if not, the same features.\n", + "Some of the tools come as chatbots on the web and others are extensions\n", + "that can be implemented in your favorite IDE. \\## VSCode and GitHub\n", + "Copilot Integration We will not cover how to use VSCode in this course,\n", + "however it is a very versatile IDE that comes with many other extension,\n", + "for example git, github and github copilot integration. There are also\n", + "other extensions for other IDE’s however we will only cover some basic\n", + "features that the GithHub Copilot extension in VSCode can do.\n", + "\n", + "Copilot Comes with the following features: - Get code suggestions as you\n", + "type - Ask questions about the code - Inline chat to generate code. -\n", + "Fix and debug code using the chat window - Generate code documentation\n", + "\n", + "[VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) [Copilot\n", + "extension](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/copilot/setup-simplified)\n", + "\\## A note on integrity If you have a non-disclosure-agreement (NDA)\n", + "with your employer, it may not always be possible to use AI for security\n", + "and integrity reasons as you may risk exposing confidential information\n", + "with third party vendors. It is highly recommended to be able to be able\n", + "to write program independently of an AI assistant. Always think before\n", + "you share data." + ], + "id": "f3d320bf-c2f6-4ebb-a5c5-6dc1dc2bb4b0" + } + ], + "nbformat": 4, + "nbformat_minor": 5, + "metadata": {} +} diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/debugging_code.ipynb b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/debugging_code.ipynb new file mode 100644 index 0000000..3bf0cd3 --- /dev/null +++ b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/debugging_code.ipynb @@ -0,0 +1,138 @@ +{ + "cells": [ + { + "cell_type": "markdown", + "metadata": {}, + "source": [ + "# Debugging Code\n", + "\n", + "## Introduction\n", + "\n", + "Have you ever had a piece of code not work the way you expected? What\n", + "did you do? You may have, asked a friend or used an AI assistant. In\n", + "this section, the following concepts are introduced - definition of a\n", + "bug, common types of bugs and debugging techniques.\n", + "\n", + "A *software bug* is an unintentional mistake or defect with a program,\n", + "this comes either from when the programmer makes a mistake in writing\n", + "the code or the code works in a way which has consequences that were not\n", + "foreseen by the programmer. Debugging is the act removing the bugs in\n", + "the software. Debugging is a normal part of programming that even\n", + "experiences developers spend a lot of time on.\n", + "\n", + "## Types of Bugs\n", + "\n", + "When writing code you are guaranteed to have bugs in your code. These\n", + "bugs can be categorized in the following three groups.\n", + "\n", + "- **Syntax errors** - this type of error occurs when the code fails\n", + " due to missing colons, missing indentation or a typo in code - some\n", + " languages like python are case sensitive meaning that the a capital\n", + " letter are different symbols.\n", + "- **Runtime errors** - e.g., dividing by zero or file not found.\n", + "- **Logical errors** - this may be the most dangerous that we need to\n", + " be careful with because this error can occur without any error\n", + " messages but it gives you the wrong result.\n", + "\n", + "## Debugging Techniques\n", + "\n", + "#### Print Debugging\n", + "\n", + "Insert print statements to check values of variables throughout the\n", + "program.\n", + "\n", + "``` python\n", + "def add(x, y):\n", + " print(f\"x = {x}, y = {y}\")\n", + " return x + y\n", + "```\n", + "\n", + "In the example above the print statement gives us feedback on what the\n", + "code is doing. The function in this example is obviously very simple,\n", + "but when we start applying more complex equations or function then\n", + "checking to see if the input variables are correct can indicate whether\n", + "there is an issue lies within the `add()` function or if the function is\n", + "given an incorrect input.\n", + "\n", + "#### Rubber Duck Debugging\n", + "\n", + "This is a technique by which you explaining your code line by line in\n", + "natural language to someone else, yourself or an inanimate object like a\n", + "rubber duck. This can help you spot your mistake in the code.\n", + "\n", + "#### Commenting Out Code\n", + "\n", + "Using comments to temporarily suppress parts of your code help you\n", + "isolate and find the bug.\n", + "\n", + "#### IDE Debugging tools\n", + "\n", + "Depending if you use an IDE, they often come with some sort of debugging\n", + "tools such as breakpoints, step into/over and variables explorers.\n", + "\n", + "#### AI Chat\n", + "\n", + "AI chat bots can help you find typo or fix logic in your code. You may\n", + "find yourself going through the steps above when using an AI assistant\n", + "to help you debug the code. However *never* assume that the code AI\n", + "gives you works the way you intend it to work.\n", + "\n", + "## Interactive Debugging Activity\n", + "\n", + "In the following code snippets, debug the code and document the\n", + "following: - What the bug is - How you found it (technique used) - What\n", + "actions you took to fix the bug\n", + "\n", + "#### Code 1\n", + "\n", + "``` python\n", + "def greet(name)\n", + " print(\"Hello, \" + Name)\n", + "greet(\"John\")\n", + "```\n", + "\n", + "#### Code 2\n", + "\n", + "``` python\n", + "import numpy as np\n", + "\n", + "x = np.linspace(0,5,100)\n", + "y = 1/x\n", + "\n", + "print(\"Result:\", y[0])\n", + "```\n", + "\n", + "#### Code 3\n", + "\n", + "``` python\n", + "def f(x):\n", + " return x**2 - 4 # Root at x = ±2\n", + "\n", + "def bisection(a, b, tol=1e-5, max_iter=100):\n", + " if f(a) * f(b) >= 0:\n", + " print(\"Bisection method fails. f(a) and f(b) should have opposite signs.\")\n", + " return None\n", + "\n", + " for i in range(max_iter):\n", + " c = (a + b) / 2\n", + " if abs(f(c)) < tol:\n", + " return c\n", + " elif f(c) * f(b) < 0:\n", + " a = c\n", + " else:\n", + " b = c\n", + " return (a + b) / 2\n", + "```\n", + "\n", + "## Reflection\n", + "\n", + "- What was the most challenging bug you found?\n", + "- What debugging method did you find most useful?" + ], + "id": "2949265c-5700-4fda-b785-ca5d7e913aa5" + } + ], + "nbformat": 4, + "nbformat_minor": 5, + "metadata": {} +} diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/intro_to_numerical_methods.ipynb b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/intro_to_numerical_methods.ipynb new file mode 100644 index 0000000..eb45ad7 --- /dev/null +++ b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/intro_to_numerical_methods.ipynb @@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ +{ + "cells": [ + { + "cell_type": "markdown", + "metadata": {}, + "source": [ + "# Numerical Methods\n", + "\n", + "Engineering\n", + "\n", + "## What is a numerical method?\n", + "\n", + "Numerical methods are techniques that transform mathematical problems\n", + "into forms that can be solved using arithmetic and logical operations.\n", + "Because digital computers excel at these computations, numerical methods\n", + "are often referred to as computer mathematics.\n", + "\n", + "## Numerical Differentiation\n", + "\n", + "Forwards difference Backwards difference\n", + "\n", + "[Read\n", + "More](https://pythonnumericalmethods.studentorg.berkeley.edu/notebooks/chapter20.00-Numerical-Differentiation.html)\n", + "\n", + "## Roots and Optimization\n", + "\n", + "Incremental Search Bisection Modified Secant Newton-Raphson\n", + "\n", + "## Numerical Integration\n", + "\n", + "Trapezoidal\n", + "\n", + "Simpson’s Rule\n", + "\n", + "[Read\n", + "More](https://pythonnumericalmethods.studentorg.berkeley.edu/notebooks/chapter21.00-Numerical-Integration.html)\n", + "\n", + "## Numerical Solutions of Ordinary Differential Equations\n", + "\n", + "Euler’s Method - Forward - Backwards\n", + "\n", + "Runge-Kutta Method\n", + "\n", + "[Read\n", + "More](https://pythonnumericalmethods.studentorg.berkeley.edu/notebooks/chapter22.00-ODE-Initial-Value-Problems.html)" + ], + "id": "47b4ca7c-5bc4-4436-9ecd-ab541d2a2bcc" + } + ], + "nbformat": 4, + "nbformat_minor": 5, + "metadata": {} +} diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/version_control.ipynb b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/version_control.ipynb new file mode 100644 index 0000000..df3aa5a --- /dev/null +++ b/tutorials/module_2/notebook_2/version_control.ipynb @@ -0,0 +1,183 @@ +{ + "cells": [ + { + "cell_type": "markdown", + "id": "1e82f8c5-1fb7-4e4d-b20c-c0be1e1e9f5b", + "metadata": {}, + "source": [ + "# Version Control Software\n", + "\n", + "## What is Version Control\n", + "\n", + "Version control is a system that tracks changes to files, enabling\n", + "developers to collaborate, manage code history, and revert to previous\n", + "versions when needed. The most used version control software (VCS) is\n", + "git. In this course git is the VCS we will be using.\n", + "\n", + "In the open-source community VCS is the - Tracks changes and history. -\n", + "Enables collaboration among developers. - Reduces errors by managing\n", + "code versions. - Supports branching and merging for parallel\n", + "development.\n", + "\n", + "In this section is divided up into two major sections. The first section\n", + "*Git* will cover the basics of how to create backups of your project.\n", + "The second section will cover how to use git with GitHub to\n", + "*collaborate* on projects.\n", + "\n", + "------------------------------------------------------------------------\n", + "\n", + "## Git\n", + "\n", + "Git is a version control program that tracks changes to files and\n", + "directories using snapshots. It is a distributed version control system,\n", + "meaning that each developer has a complete copy of the repository on\n", + "their local computer. Git is the most widely used version control system\n", + "and is popular among developers for its speed, flexibility, and\n", + "efficiency.\n", + "\n", + "### The Three States\n", + "\n", + "Pay attention now — here is the main thing to remember about Git if you\n", + "want the rest of your learning process to go smoothly. Git has three\n", + "main states that your files can reside in: modified, staged, and\n", + "committed:\n", + "\n", + "- **Modified** means that you have changed the file but have not\n", + " committed it to your database yet.\n", + "- **Staged** means that you have marked a modified file in its current\n", + " version to go into your next commit snapshot.\n", + "- **Committed** means that the data is safely stored in your local\n", + " database.\n", + "\n", + "This leads us to the three main sections of a Git project: the working\n", + "tree, the staging area, and the Git directory.\n", + "\n", + "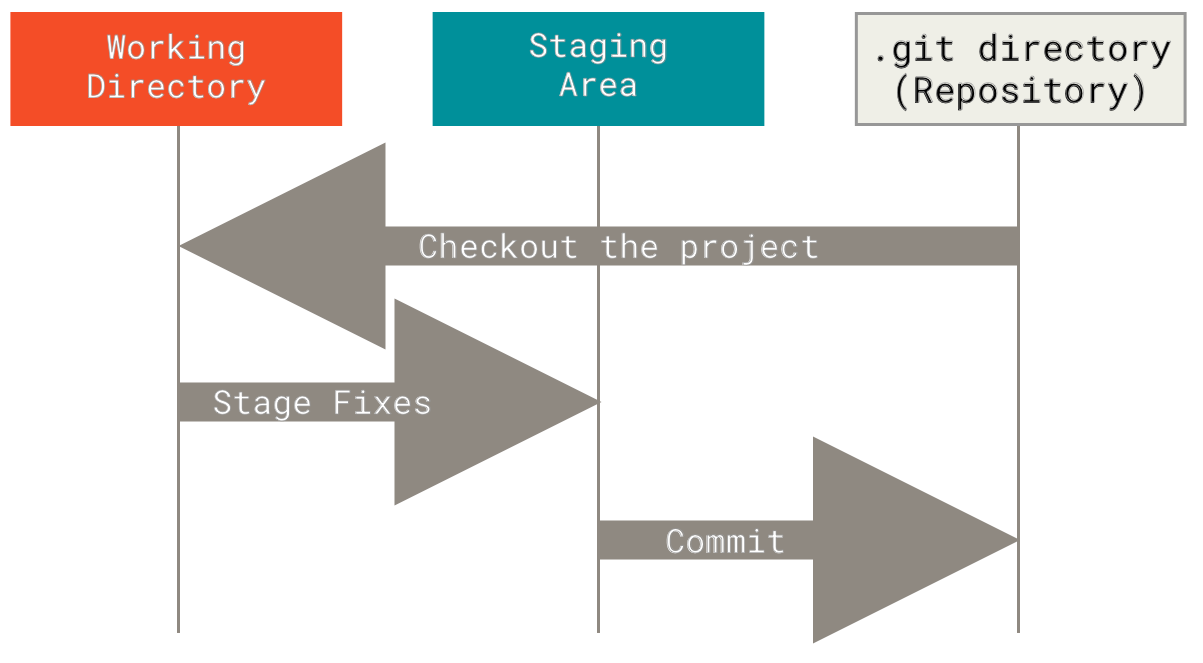\n", + "\\### Branching In git, branches allow for parallel workflow on a\n", + "project. It give contributors the ability to work different features at\n", + "the same time. Each branch represents an independent line of\n", + "development, and once a feature or fix is complete, it can be merged\n", + "back into the main branch. Here is a common branching structure used in\n", + "many Git projects: - Main Branch - The main branch (a.k.a. master\n", + "branch) is the default branch in a Git repository and contains the\n", + "stable version of the code. - Development Branch - is created to develop\n", + "a new feature or fix a bug without affecting the main branch. It isn’t\n", + "necessarily always stable, but whenever it gets to a stable state, it\n", + "can be merged into master. - Topic Branch - A topic branch is a\n", + "short-lived branch that you create and use for a single particular\n", + "feature or related work. 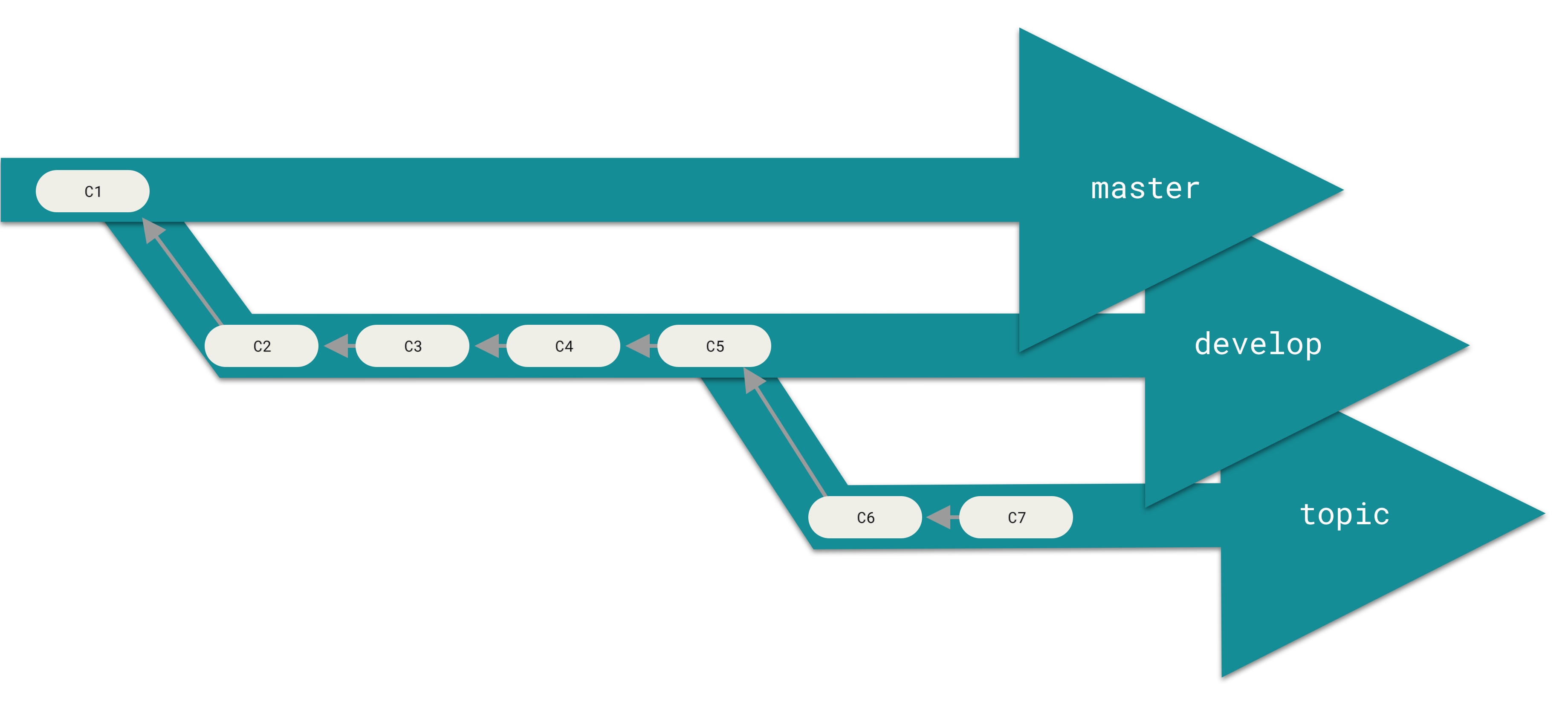 \\###\n", + "Best Practices - Use descriptive commit messages. - Commit early and\n", + "often. - Keep commits focused on a single change. - Use feature branches\n", + "for new features or bug fixes. - Review and test changes before\n", + "merging. - Resolve conflicts promptly. - Keep the commit history clean\n", + "and organized.\n", + "\n", + "### Basic Commands\n", + "\n", + "Here is a list of some git commands to get you started. \\#### Starting\n", + "your repository - `git init` - Initialize a new Git repository. -\n", + "`git clone` - Clone an existing repository. \\#### Committing -\n", + "`git status` - Check the status of the repository. - `git add` - Add\n", + "files to the staging area. - `git commit` - Commit changes to the\n", + "repository. \\#### Branching - `git branch` - List, create, or delete\n", + "branches. - `git checkout` - Switch between branches. \\####\n", + "History/Inspection - `git log` - View the commit history. \\####\n", + "Collaborative - `git fetch` - Fetches updates from a remote but does not\n", + "merge. - `git merge` - Merge changes from a named commit to the current\n", + "branch. - `git pull` - Fetch and merge changes from a remote\n", + "repository. - `git push` - Push changes to a remote repository.\n", + "\n", + "### More on git\n", + "\n", + "Interested in learning more about git? Here’s a free book that teaches\n", + "you everything about git and how to use it at a professional level.\n", + "Available as both HTML and PDF download: [Git\n", + "Pro](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2).\n", + "\n", + "## GitHub - The collaborative platform\n", + "\n", + "GitHub is a web-based platform that hosts Git repositories and provides\n", + "collaboration tools for developers. It allows developers to share code,\n", + "track issues, and collaborate on projects with other developers. GitHub\n", + "is widely used for open-source projects, team collaboration, and code\n", + "hosting. \\### GitHub Features - Remote Repository Hosting - GitHub\n", + "allows you to host projects and code remotely on their servers. -\n", + "Issues - Issues are used to track bugs, feature - Pull Requests -\n", + "Internal request system for contributors to request code to be pulled.\n", + "\\### Workflow Depending on the size of the project and whether the\n", + "project is closed- or open-source, the workflow of the project will\n", + "differ. In this section we cover some git workflow models and the model\n", + "you’re going to be using for this course.\n", + "\n", + "**Centralized**: The project has only one central hub or *repository*,\n", + "can accept code and everybody synchronizes their work with it. This\n", + "model is suitable for small and closed-sourced projects. 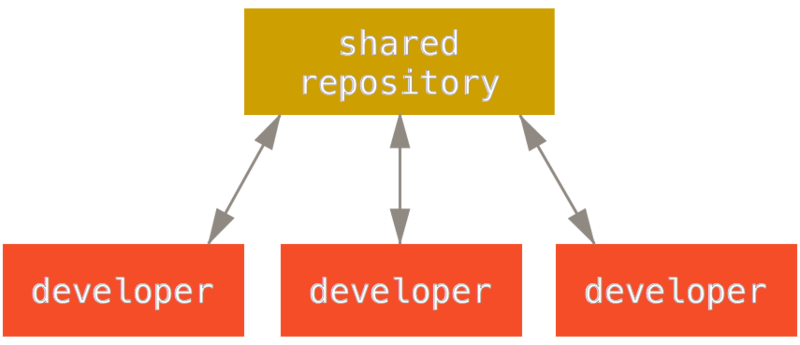\n", + "\n", + "**Integration-Manager:** There are multiple public variants of the code\n", + "original code known as *forks*. The integration manager can decide what\n", + "features to pull from the forks. This is the model that is similar to\n", + "the one used on GitHub 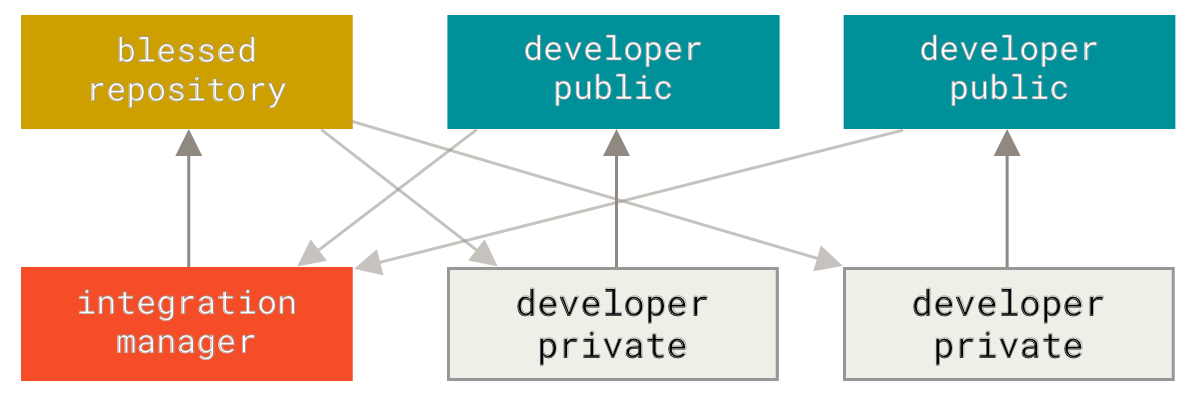\n", + "\n", + "**Dictator and Lieutenants Workflow:** This is similar to the\n", + "integration-manager model, however due to the size of the project. A\n", + "rank of integration managers is formed. one example of this is the\n", + "development of the Linux kernel. 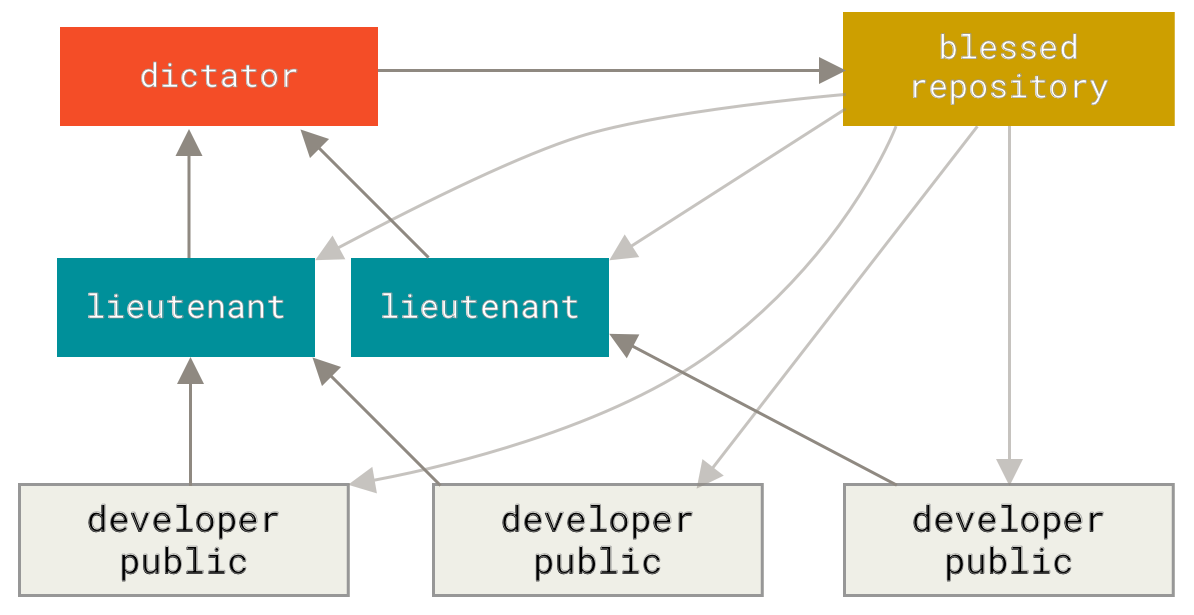\n", + "\n", + "GitHub is designed around a particular collaboration workflow, centered\n", + "on Pull Requests. This flow works whether you’re collaborating with a\n", + "tightly-knit team in a single shared repository, or a\n", + "globally-distributed company or network of strangers contributing to a\n", + "project through dozens of forks. It is centered on the Topic Branches\n", + "workflow covered in Git Branching.\n", + "\n", + "Here’s how it generally works: 1. Fork the project. 2. Create a topic\n", + "branch from master. 3. Make some commits to improve the project. 4. Push\n", + "this branch to your GitHub project. 5. Open a Pull Request on GitHub. 6.\n", + "Discuss, and optionally continue committing. 7. The project owner merges\n", + "or closes the Pull Request. 8. Sync the updated master back to your\n", + "fork.\n", + "\n", + "### Terms\n", + "\n", + "- Pull Request - A *pull request* is a request to merge changes from a\n", + " feature branch into the main branch or from a forked repository to\n", + " the original or “upstream” repository.\n", + "- Merge - A *merge* combines the changes from one branch into another\n", + " branch.\n", + "- Conflict - A *conflict* occurs when Git cannot automatically merge\n", + " changes and requires manual intervention.\n", + "\n", + "### Code resource - Using GitHub to re-use existing code.\n", + "\n", + "In your engineering career, you will most likely use a computation\n", + "method that has been come up with before. In such scenarios, open-source" + ] + } + ], + "metadata": { + "kernelspec": { + "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)", + "language": "python", + "name": "python3" + }, + "language_info": { + "codemirror_mode": { + "name": "ipython", + "version": 3 + }, + "file_extension": ".py", + "mimetype": "text/x-python", + "name": "python", + "nbconvert_exporter": "python", + "pygments_lexer": "ipython3", + "version": "3.13.2" + } + }, + "nbformat": 4, + "nbformat_minor": 5 +} |
