diff options
| author | Christian Kolset <christian.kolset@gmail.com> | 2025-04-24 23:31:17 -0600 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Christian Kolset <christian.kolset@gmail.com> | 2025-04-24 23:31:17 -0600 |
| commit | c98972ced700b6250915a21af4b76459365743f3 (patch) | |
| tree | 87f62caa9dbe5dbb997f12f7e167ff4ddbc91697 /tutorials/module_2 | |
| parent | 342b88e6002fa1eee9b020864d83ddbd79ef3ad9 (diff) | |
Updated markdown files to look better after converting to latex files.
Diffstat (limited to 'tutorials/module_2')
| -rw-r--r-- | tutorials/module_2/ai_assisted_programming.md | 6 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | tutorials/module_2/problem_solving_strategies.md | 18 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | tutorials/module_2/version_control.md | 11 |
3 files changed, 19 insertions, 16 deletions
diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/ai_assisted_programming.md b/tutorials/module_2/ai_assisted_programming.md index bccedbd..86be2d7 100644 --- a/tutorials/module_2/ai_assisted_programming.md +++ b/tutorials/module_2/ai_assisted_programming.md @@ -2,10 +2,12 @@ ## What is it? Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been around for a long time. However, not until recently did engineers make it easy and "fun" to work with. By now you probably have a pretty good idea of what AI can do. However, you may not have used an AI assistant before. As the name suggests, an AI assistant can help you develop code, speed up your writing with code suggestions and allows you to focus on solving the problem at hand rather. AI is a technology that is constantly improving. As engineers we need to *understand* how we can use AI as a tool to achieve our goals more efficiently. This section cover good practices of how we can implement AI and lists some AI assistant tools that we can use. + ## Good vs. Bad uses of AI Don't try to get AI to do work *for you* but *with you*. You need to understand what you're doing. If you don't understand what the AI is doing, then you're not in control of the work. You're not going to go far until something unexpected happens. AI is a great learning tool, research as show that students can benefit from using AI as personal tutor [more](https://hbsp.harvard.edu/inspiring-minds/ai-as-personal-tutor). + ## Available tools Below is a comprehensive list of tools that are available at not cost to you. @@ -22,6 +24,7 @@ Below is a comprehensive list of tools that are available at not cost to you. | Codeium | Free | | aiXcoder | Free | Many of the tools above come with similar, if not, the same features. Some of the tools come as chatbots on the web and others are extensions that can be implemented in your favorite IDE. + ## VSCode and GitHub Copilot Integration We will not cover how to use VSCode in this course, however it is a very versatile IDE that comes with many other extension, for example git, github and github copilot integration. There are also other extensions for other IDE's however we will only cover some basic features that the GithHub Copilot extension in VSCode can do. @@ -34,5 +37,6 @@ Copilot Comes with the following features: [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) [Copilot extension](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/copilot/setup-simplified) -## A note on integrity + +## A note on intellectual property If you have a non-disclosure-agreement (NDA) with your employer, it may not always be possible to use AI for security and integrity reasons as you may risk exposing confidential information with third party vendors. It is highly recommended to be able to be able to write program independently of an AI assistant. Always think before you share data.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/problem_solving_strategies.md b/tutorials/module_2/problem_solving_strategies.md index 1a50aec..50216ab 100644 --- a/tutorials/module_2/problem_solving_strategies.md +++ b/tutorials/module_2/problem_solving_strategies.md @@ -8,8 +8,8 @@ By the end of this lesson, students will be able to: - Translate engineering problems into structured programming logic. - Use software tools to implement, test, and refine engineering solutions. ---- -## 1. Define the Problem + +## Define the Problem Like many other classes we need to frame the problem before working it. So before jumping straight into coding or building models, clearly define the engineering problem. @@ -17,8 +17,8 @@ Like many other classes we need to frame the problem before working it. So befor - **Establish system constraints and assumptions.** Identify physical laws, design requirements, and performance limits. - **Clarify computational objectives.** What are you trying to calculate, simulate, or optimize? ---- -## 2. Think Algorithmically + +## Think Algorithmically Since we are going to use computers to calculate our solution we first need to break the problem into logical steps that a computer can follow. @@ -33,8 +33,8 @@ Since we are going to use computers to calculate our solution we first need to b 3. Plot the stress-strain curve. 4. Identify the yield point or modulus. ---- -## 3. Write & Execute the Code + +## Write & Execute the Code - **Choose the right tools.** Are there libraries I can use to get to my objective more effectively? - **Write modular code.** Use functions to separate different tasks (e.g., reading data, computing values, plotting). @@ -42,8 +42,8 @@ Since we are going to use computers to calculate our solution we first need to b **Example:** Write a Python script that uses NumPy and Matplotlib to load a CSV file, compute stress and strain, and generate plots. ---- -## 4. Test and Validate + +## Test and Validate - **Assess the feasibility of your results.** Do the values align with expected physical behavior? - **Compare against established benchmarks.** Validate solutions using experimental data, literature values, or known theoretical limits. @@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Since we are going to use computers to calculate our solution we first need to b **Example:** If your plot shows stress values in the thousands when you expect hundreds, check unit conversions in your formula. ---- + ## Case Study: Simulating a Spring-Mass System **Scenario:** Model the motion of a mass-spring-damper system using a numerical solver. diff --git a/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md b/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md index 78b90db..7d633a5 100644 --- a/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md +++ b/tutorials/module_2/version_control.md @@ -11,7 +11,6 @@ In the open-source community VCS is the In this section is divided up into two major sections. The first section *Git* will cover the basics of how to create backups of your project. The second section will cover how to use git with GitHub to *collaborate* on projects. ---- ## Git Git is a version control program that tracks changes to files and directories using snapshots. It is a distributed version control system, meaning that each developer has a complete copy of the repository on their local computer. Git is the most widely used version control system and is popular among developers for its speed, flexibility, and efficiency. @@ -24,13 +23,13 @@ Pay attention now — here is the main thing to remember about Git if you want t This leads us to the three main sections of a Git project: the working tree, the staging area, and the Git directory. -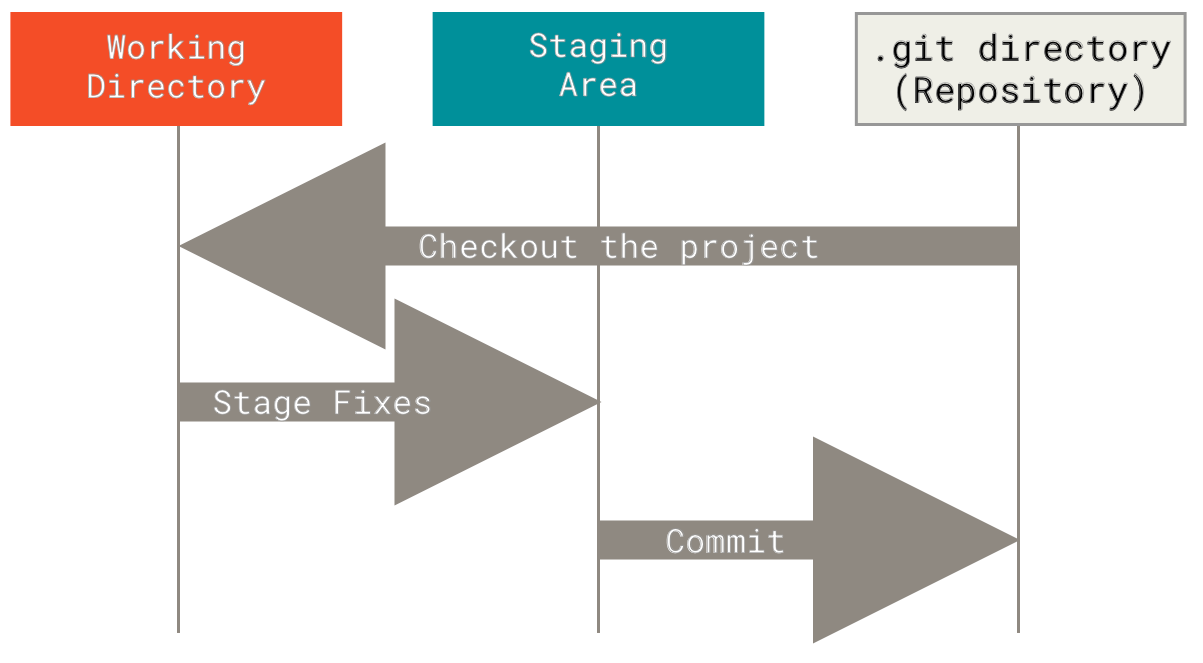 + ### Branching In git, branches allow for parallel workflow on a project. It give contributors the ability to work different features at the same time. Each branch represents an independent line of development, and once a feature or fix is complete, it can be merged back into the main branch. Here is a common branching structure used in many Git projects: - Main Branch - The main branch (a.k.a. master branch) is the default branch in a Git repository and contains the stable version of the code. - Development Branch - is created to develop a new feature or fix a bug without affecting the main branch. It isn’t necessarily always stable, but whenever it gets to a stable state, it can be merged into master. - Topic Branch - A topic branch is a short-lived branch that you create and use for a single particular feature or related work. -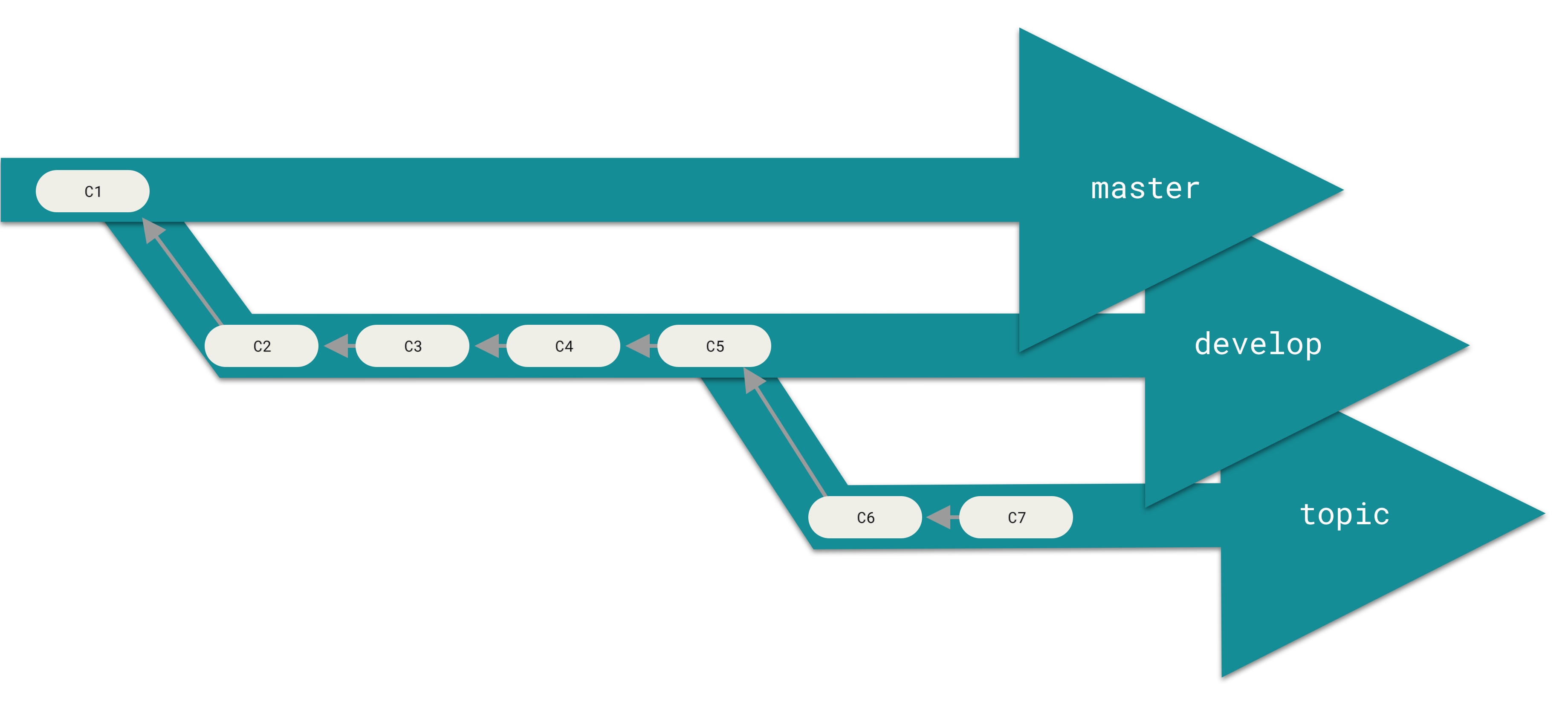 + ### Best Practices - Use descriptive commit messages. - Commit early and often. @@ -75,17 +74,17 @@ Depending on the size of the project and whether the project is closed- or open- **Centralized**: The project has only one central hub or *repository*, can accept code and everybody synchronizes their work with it. This model is suitable for small and closed-sourced projects. -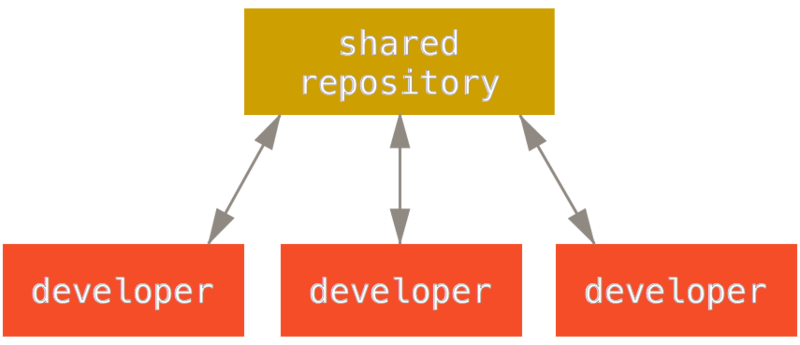 + **Integration-Manager:** There are multiple public variants of the code original code known as *forks*. The integration manager can decide what features to pull from the forks. This is the model that is similar to the one used on GitHub -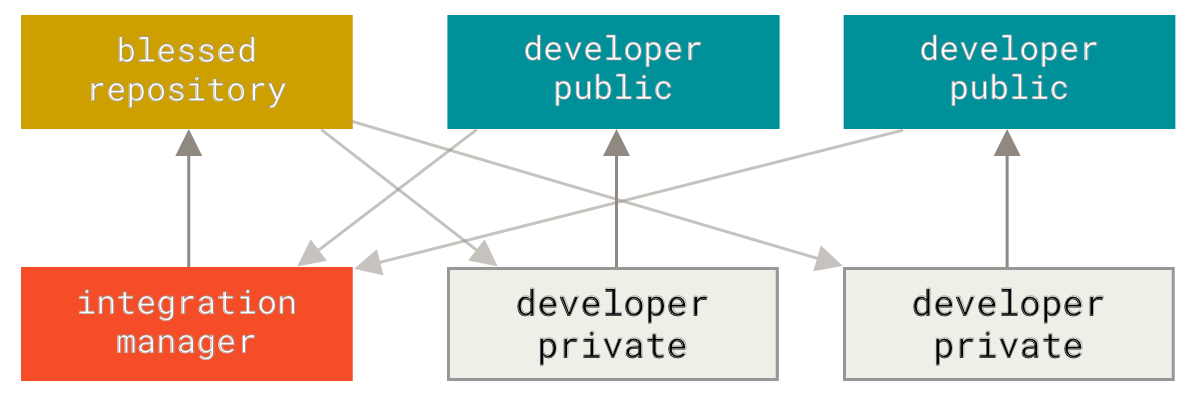 + **Dictator and Lieutenants Workflow:** This is similar to the integration-manager model, however due to the size of the project. A rank of integration managers is formed. one example of this is the development of the Linux kernel. -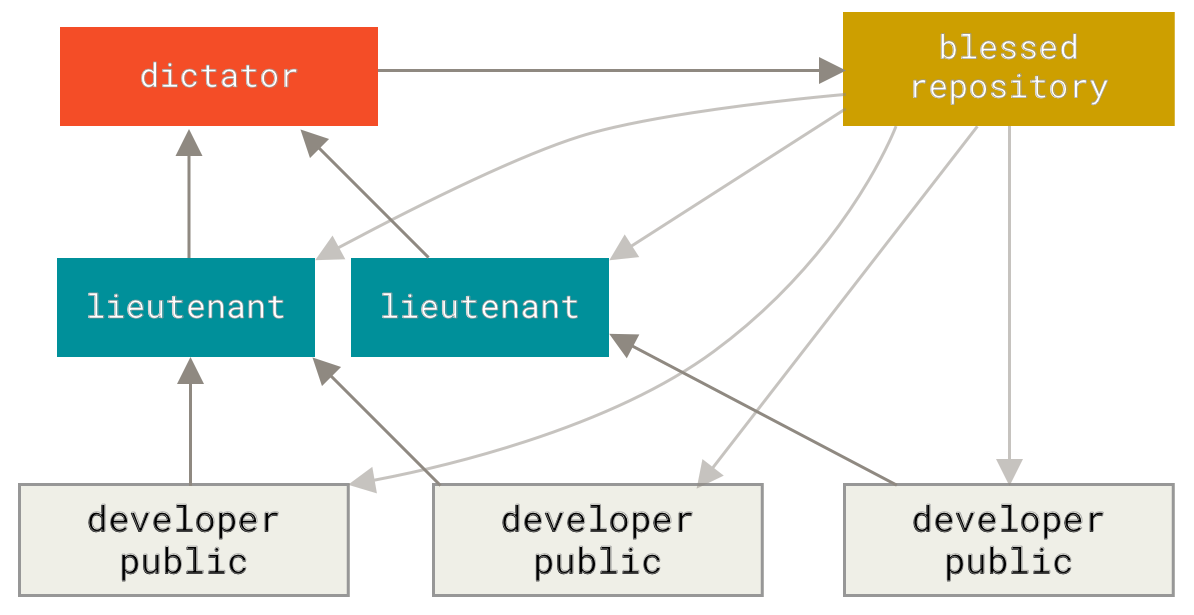 + GitHub is designed around a particular collaboration workflow, centered on Pull Requests. This flow works whether you’re collaborating with a tightly-knit team in a single shared repository, or a globally-distributed company or network of strangers contributing to a project through dozens of forks. It is centered on the Topic Branches workflow covered in Git Branching. |
